Docusign eSignature Integration 101: Implementing JWT authentication and sending your first envelope
Learn how to set up authentication for a solution that connects Docusign APIs to your Google Sheets, Docs, and Forms to provide powerful, script-based automation.

In the modern workplace, Google Workspace (including Google Sheets, Docs, and Forms) often serves as a central hub for business operations. Connecting the power of Docusign Agreement APIs to Googleʼs environment via Google Apps Script enables powerful, script-based automation. For example, you can easily integrate Google Workspace with the Docusign eSignature REST API to generate eSignature contracts based on Google Sheets data. You can also track eSignature envelope status and contract metadata and expose this information in your Looker Studio dashboard.
The main hurdle in this integration is authentication. Since Apps Script runs in a serverless environment and cannot easily handle browser redirects, the standard Authorization Code Grant flow is impractical. The perfect solution? JSON Web Token (JWT) Grant.
A JWT is composed of a header, a payload, and a signature. The signature is created via an RS256 algorithm based on your RSA private key. Google Apps Scriptʼs native environment lacks a straightforward, built-in function to perform this complex signing operation.
To implement JWT Grant authentication with Docusign within a Google Apps Script project, we are using the open-source JavaScript cryptography library jsrsasign.
You will need the following from your Docusign developer (demo) or production account:
Integration key (client ID): Created via the Docusign Apps and Keys page. See Configure your app for details about creating integration keys and their associated settings.
RSA key pair: Generated during the integration key setup. This key is used to sign the JWT.
User ID: The unique GUID for the user you wish to impersonate.
Google Apps Script project: Access your script editor from a Google Sheet, Doc, or even a Form, or navigate directly to https://script.google.com.
You must manually construct this URL and have the user whose ID is in your script open it in a browser, log in with your Docusign user account, and select Accept.
URL structure (developer environment example)
https://account-d.docusign.com/oauth/auth?
response_type=code&
scope=signature%20impersonation&
client_id={YOUR_INTEGRATION_KEY}&
redirect_uri={A_REGISTERED_REDIRECT_URI}scope: Must include signature and impersonation if we are focusing on the eSignature API. For other Docusign APIs, make sure to use the relevant authentication scope.
redirect_uri: Must be a URI (like http://localhost/ or a custom URL) that you have pre-registered for your integration key in the Docusign administration panel. See Redirect URI for details.
Google Apps Script doesn't natively support the necessary RSA signature functions for JWTs. The solution is to use the popular jsrsasign library.
In your Apps Script project, include the global variables navigator and window to ensure library compatibility.
Load jsrsasign-all-min.js, available on the KJUR GitHub repository.
var navigator = {}; // Fake a navigator object for the jsrsasign lib
var window = {}; // Fake a window object for the jsrsasign lib
// Importing : https://github.com/kjur/jsrsasign/blob/master/jsrsasign-all-min.js
eval(UrlFetchApp.fetch('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kjur/jsrsasign/refs/heads/master/jsrsasign-all-min.js').getContentText());This function uses your Docusign credentials and the imported jsrsasign library to generate the cryptographic signature for the JWT.
/**
* Generates a signed JSON Web Token (JWT) required for Docusign JWT Grant.
* @return {string} The signed JWT.
*/
function generateDocusignJWT() {
// Docusign configuration parameters
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_INTEGRATION_KEY"; // Docusign integration key
const USER_ID = "YOUR_USER_ID"; // Docusign user ID (GUID)
const AUTH_SERVER = "account-d.docusign.com"; // Use "account-d.docusign.com" for the developer environment, "account.docusign.com" for production
// NOTE: Private key MUST be formatted as a single-line string with escaped newlines.
const PRIVATE_KEY = `-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIICXQIBAAKBgQ...
...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----`;
// JWT timing (standard practice)
const iat = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000); // Current timestamp in seconds (Issued At)
const exp = iat + 3600; // Expiration in 1 hour
// 1. JWT header
const header = {
alg: "RS256",
typ: "JWT"
};
// 2. JWT payload
const payload = {
iss: CLIENT_ID, // Integration key
sub: USER_ID, // User ID being impersonated
aud: AUTH_SERVER, // Authentication server
iat: iat, // Issued At claim identifies the time of issuance in epoch time
exp: exp, // Expiration time for the JWT assertion when assertion should not be accepted anymore for processing
scope: "signature impersonation" // List of possible scopes is available from https://developers.docusign.com/platform/auth/reference/scopes/
};
// 3. Signing the JWT using jsrsasign
var sHeader = JSON.stringify(header);
var sPayload = JSON.stringify(payload);
// https://kjur.github.io/jsrsasign/api/symbols/KJUR.jws.JWS.html#.sign
var signedJWT = KJUR.jws.JWS.sign("RS256", sHeader, sPayload, PRIVATE_KEY);
console.log("sJWT: "+ signedJWT);
return signedJWT;
}The signed JWT is sent to the Docusign token endpoint to retrieve the temporary access token.
/**
* Retrieves a Docusign access token using the generated JWT.
* @return {string} The Docusign access token.
*/
function getDocusignAccessToken() {
const jwt = generateDocusignJWT();
const url = "https://account-d.docusign.com/oauth/token";
const options = {
method: "POST",
contentType: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
payload: {
grant_type: "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer",
assertion: jwt
}
};
// UrlFetchApp handles the HTTP POST request
const response = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
const json = JSON.parse(response.getContentText());
if (json.error) {
Logger.log("Error: " + json.error + " - " + json.error_description);
throw new Error("Docusign Token Error: " + json.error_description);
}
return json.access_token;
}Every subsequent Docusign API call requires an account ID and a unique base path (URI). The userinfo endpoint provides these details.
/**
* Retrieves Docusign userinfo and extracts the base path required for API calls.
* * @return {object} An object containing the accountId, baseUri, and accessToken.
*/
function getDocusignUserInfoAndBasePath() {
const token = getDocusignAccessToken();
const USERINFO_URL = "https://account-d.docusign.com/oauth/userinfo";
const options = {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + token
},
muteHttpExceptions: true
};
try {
const response = UrlFetchApp.fetch(USERINFO_URL, options);
const responseCode = response.getResponseCode();
const responseText = response.getContentText();
if (responseCode !== 200) {
Logger.log("Response Text: " + responseText);
throw new Error("Failed to retrieve Docusign UserInfo.");
}
const userInfo = JSON.parse(responseText);
// Check if the accounts array exists and is not empty
if (!userInfo.accounts || userInfo.accounts.length === 0) {
throw new Error("User is authenticated but has no active Docusign accounts linked.");
}
// Find the default account for API calls
const defaultAccount = userInfo.accounts.find(account => account.is_default);
if (!defaultAccount) {
throw new Error("User has no default Docusign account.");
}
// The base URI must include the /restapi/v2.1 segment
const baseUri = defaultAccount.base_uri + "/restapi/v2.1";
Logger.log("Docusign Connection Successful!");
Logger.log("Base API URI: " + baseUri);
return {
accountId: defaultAccount.account_id,
baseUri: baseUri,
accessToken: token // Useful to return the token alongside the URIs
};
} catch(e) {
Logger.log("API Call Failed: " + e.message);
throw e;
}
}
// Final test function: Call this function to start your Docusign integration
function startDocusignAutomation() {
const credentials = getDocusignUserInfoAndBasePath();
// Now you can use credentials.baseUri, credentials.accountId and credentials.accessToken
// to build your requests (e.g., sending an envelope).
Logger.log("Ready to make API calls using Account ID: " + credentials.accountId);
}Let’s try this script by launching the startDocusignAutomation() function in our Google Apps Script environment and checking the execution log to see if we are able to obtain our account ID:
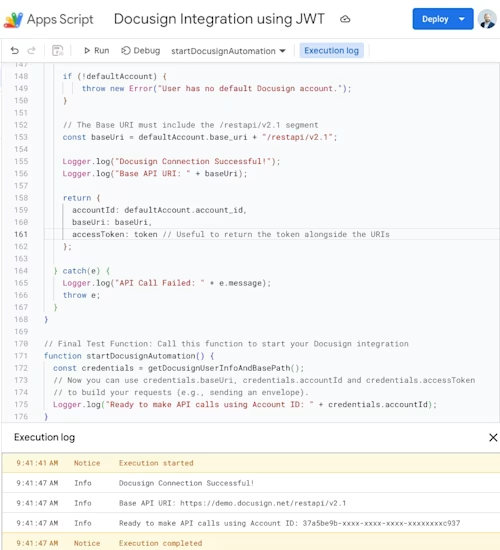
If the account ID appears as shown above, the script succeeded.
This post guided you through setting up a robust, non-interactive integration between Google Workspace and the Docusign Agreement APIs. We specifically managed the authentication process in a serverless environment like Google Apps Script by implementing the secure JWT Grant flow.
As your next steps, learn more about our Agreement APIs and start building your own use cases. For example, use the startDocusignAutomation() function and the credentials object to generate eSignature contracts based on Google Sheets data. We recommend exploring the following guides for this type of integration:
Review the specifications for the jsrsasign cryptographic library used for JWT signing.
Learn more about JWT Grant authentication.
Review the full list of required authentication scopes.
Get the details about the userinfo endpoint.

Arnaud Lesueur has been with Docusign since 2015 in various presales roles within EMEA. Over the years, he's been working with hundreds of our customers to digitalize their agreement processes. With a strong background across the complete Docusign portfolio, Arnaud received his Gold Certified Presales Agreement Cloud Expert designation in 2023. Arnaud can be reached at arnaud.lesueur@docusign.com.
Related posts
